life cycle of a seedless plant
Which adult phase is dominant. They have an alternation of generations not unlike the bryophytes the seedless nonvascular plants.

Bio 2 Exam 2 Flashcards Quizlet Plant Life Cycle Alternation Of Generations Vascular Plant
The fern life cycle illustrates sexual reproduction in the seedless vascular plants.

. Plants alternate between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte generations and between sexual and asexual reproduction. SCIBIO657 Life Cycle of Seedless Vascular Plants - Biology. A mature sporophyte fern has the familiar leafy fronds.
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase. Remember that the moss life cycle is characterized by two types of haploid spores male and female. General life cycle of a seedless vascular plant.
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase. The spores will grow into new plants when the environment is suitable. Following fertilization the sporophyte forms.
This then grows into a sporophyte. The gametophyte is now less conspicuous but still independent of the sporophyte. Are either phases dependent on the other.
The ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually gives plants the flexibility to adapt to changing environments. The life cycle of nonvascular seedless plants can be described as follows. Recall the sporophytic generation is the diploid part of the life cycle and via meiosis haploid spores are produced.
Sporangia produce spores that develop into tiny heart-shaped. When spores land they grow into gametophytes. In seedless vascular plants the diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle.
Seedless plants can reproduce asexually or sexually. The life cycle pattern in both Pteridophyta and Spermatophyta is basically same. In addition the stem tip in most lycophytes forks repeatedly resulting in branches that are of about equal length whereas in higher plants there is a single main axis from which lateral branches arise.
The life cycle of all plants is complex because it is characterized by alternation of generations. Though the life of a nonvascular seedless plant is a cycle this can be considered the initial step in the life cycle. What is the sporophyte and gametophyte stage.
New answers Rating There are no new answers. Plant reproduction Other contents. The diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle while the gametophyte is an inconspicuous but still-independent organism.
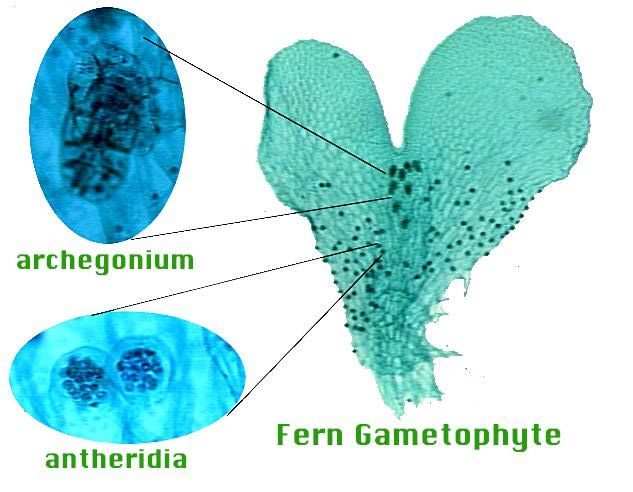
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants shows an Alternation of Generations. This gametophyte contains the antheridia male sex organ and the archegonia female sex organ together on one plant. -sperm are produced in antheridia.
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants alternates between a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte phase. Seedless vascular plants still depend on water during fertilization as the flagellated sperm must swim on a layer of moisture to reach the egg. Seeds are easy to see while spores can be nearly invisible to the naked eye.
Eggs are produced in archegonia -fertilization still requires water -multicellular embryo is retained by the female parent -spores are produced in sporangia. Draw the diagrams of the life-cycles of non-vascular plants and seedless vascular plants and. During the life cycle of a seedless plant a sporophyte releases spores.
Seedless vascular plants reproduce through unicellular haploid spores instead of seeds. Draw the diagrams of the life-cycles of non-vascular plants and seedless vascular plants and compare the differences between them in words. The gametophyte is now less conspicuous but still independent of the sporophyte.
Comments There are no comments. Name 2 seedless vascular plants and describe the importance of seedless vascular plants. In the sporophyte stage plants make spores.
Their complex life cycle allows for great. The sporophyte is connected to and dependent on the gametophyte. Label as much as you can.
In seedless vascular plants the diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle. First the sporangium releases many spores formed by meiosis which germinate in moist soil to form a haploid gametophyte. Seeds are considered to be a key adaptation for reproduction in a land habitat.
Seedless vascular plants still depend on water during fertilization as the flagellated sperm must swim on a layer of moisture to reach the egg. The dominant part of the fern life cycle is the diploid sporophyte generation -. In the life cycle of a fern the sporophyte generation is dominant.
Pteridophytes ferns are the seedless vascular plants. Life cycle of seedless plant Life cycle of moss and fern ID. When a small fragment of the plant is broken off it can form a new plant.
What Types of Plants Produce Seeds. The undersides of the leaves are dotted with clusters of sporangia. Figure below shows a typical fern life cycle.
Gametophyte life cycle seedless vascular plants 2 more sporangia sporophyte. The seeds are complex in their cellular structure. Seeds can last for years before sprouting making them a viable resource to carry and plant in other regions long after they have left the parent plant.
The diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle while the gametophyte is an inconspicuous but still-independent organism. The lightweight spores allow for easy dispersion in the wind. Like all plants seedless vascular plants have a gametophytic generation and a sporophytic generation.
The sporophyte produces spores that will develop into gametophytes and start the cycle over again. The majority of living plants produce seeds and are divided into two large groups the gymnosperms and angiosperms. The difference between spores and seeds is plentiful.
Like all seedless plants the lycophytes require water for the sperm to swim to the egg. The plants in Division Pteridophyta are seedless. Seedless vascular plants include clubmosses and ferns.
1The male gametophyte produces flagellated sperm that must swim to. These do not multiply by seeds as the plants in Division Spermatophyta. Life cycle Add to my workbooks 5 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog.
One gametophyte produces sperm cells that fertilize the egg cells of another gametophyte forming a. Research and citations are required. Some seedless plants like hornworts and liverworts can reproduce asexually through fragmentation.
Describe the 2 stages of a plants life cycle.

Life Cycle Of Seedless Vascular Plants Ck 12 Foundation Vascular Plant Life Cycles Vascular
Page Not Found Alternation Of Generations Biology Lessons Vascular Plant

Plant Diversity Botany Plant Classification Plant Science

Lab Ch 16 Non Vascular Plants And Seedless Vascular Plants Biology 152 With Kinnes At Azusa Pacific University Studyblue Vascular Plant Vascular Plants

Fern Life Cycle Fern Life Cycle Plant Life Cycle Life Cycles

Moss Life Cycle ช วว ทยา การเร ยนร พ นหล ง

Copy Of Copy Of Vascular And Non Vascular Plants Teaching Plants Plant Activities Plant Science

Plants Ii Non Vascular And Seedless Vascular Plants Biol110f2012 Confluence Vascular Plant Vascular Plants

Bil 226 Lecture 14 Biology Plants Plants Vocabulary Life Cycles

Life Cycle Of The Fern Candace Jordan Class Plant Life Cycle Ferns Life Cycles

Middle Grades Plants Are At The Basis Of The Food Chain Where Would We Be Without Them And Look At That Diversity Biology Plants Teaching Plants Plants

Bryophyte Life Cycle Stages Life Cycle Stages Plant Science Life Cycles

Plantyhamchuk March 2015 Sexually Excited Moss C Mcgraw Hill Via Molecular Ecologist Life Cycles Plant Life Cycle Biology Lessons

Pin By Dandavats Dasa Flores On Botany Vascular Plant Development Faith

Life Cycle Definition Types Facts Life Cycles Fern Life Cycle Cycle Drawing

Fern Plants And Their Life Cycle Seedless Vascular Updated Plants Fern Plant Ferns

Fern Life Cycle Biology Plants Fern Life Cycle Teaching Plants

